Improved Reconnaissance Capabilities through Multidimensional Radar Imaging
More precise results in the detection and classification of ground objects by airborne radar systems: Research at Fraunhofer FHR has shown that valuable additional information about a scene can be gained through multidimensional radar imaging. The institute is working on this topic on behalf of the German Armed Forces and is participating in NATO research task groups on the subject.
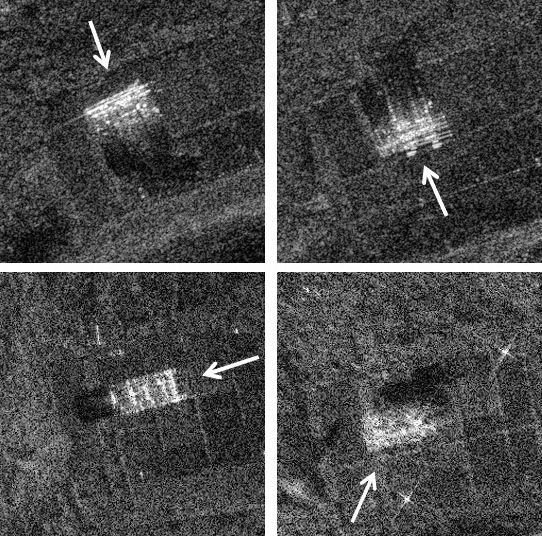
In crisis situations, airborne reconnaissance of the ground situation is essential. The use of SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) systems in combination with high-resolution imaging radar techniques already provides helpful results today. But how can reconnaissance performance be improved? How can images be made more precise and more information about objects such as military vehicles and buildings be obtained? In this context, researchers at Fraunhofer FHR investigated the added value of imaging radar techniques for object classification when looking at the scene from different directions during airborne SAR data acquisitions, using multiple frequencies (Ka-band and W-band), and multiple polarizations. The developed theories and algorithms were tested in a practical setting during an international measurement campaign, in which Fraunhofer FHR participated with the MIRANDA-94 and Pamir-Ka systems, at a military test site of the Royal Air Force in England.
Positive effects through different perspectives, frequencies, and polarizations
The results are promising: The collected data clearly show that the use of multidimensional radars results in positive effects for target detection and recognition. Both different viewing angles and changed frequencies at the same viewing angle, as well as different polarizations, provide additional information that can be crucial for identifying, for example, a specific type of tank.
The work has resulted in numerous publications, including a 300-page technical report and two books to which Fraunhofer FHR contributed. The NATO also acknowledged the excellent work of the researchers in the NATO Research Task Group SET-250 by awarding the NATO SET Panel Excellence Award. Based on the insights into multidimensional radar imaging, the institute is now focusing on improving and miniaturizing the systems, among other things, to develop and test their use on drones with compact sensors.